Now in The Journal of Neuroscience: New Protective Marker in Dopamine Neurodegeneration in the Brain
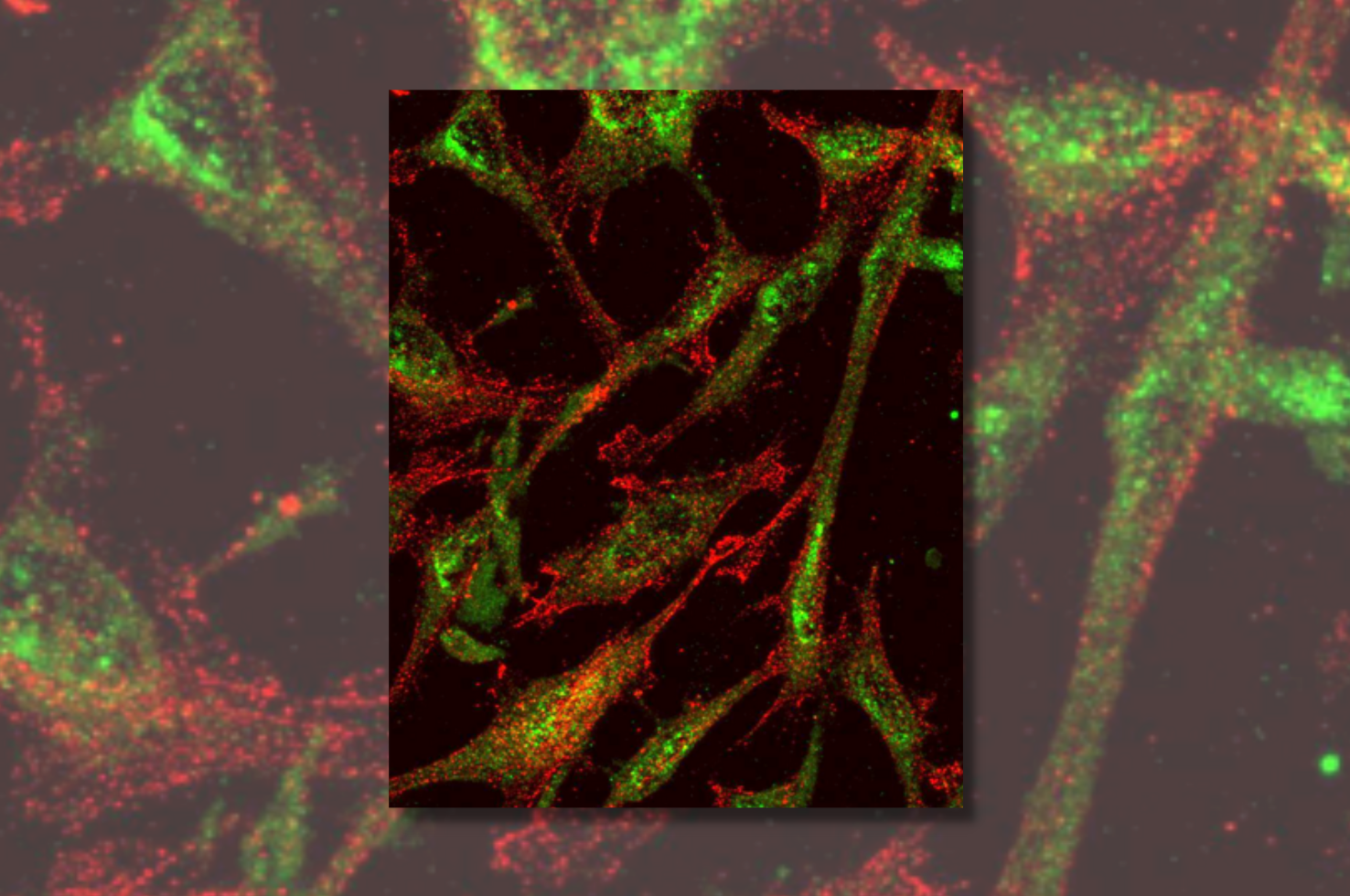
Parkinson's disease, a nervous system disorder that affects movement, is characterized by progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta in the midbrain. By contrast, the midbrain ventral tegmental area does not experience loss of dopaminergic neurons, though the explanation for the neurons’ resilience in this region has not been sufficiently studied. One possible explanation involves the expression of the vesicular glutamate transporter 2 in the ventral tegmental area, which may modify resilience to neurodegeneration.
In a recent Journal of Neuroscience study, University of Pittsburgh investigators including PhD student Silas Buck, the paper’s first author, as well as Kenneth Fish, PhD (Associate Professor of Psychiatry), and senior author Zachary Freyberg, MD, PhD (Assistant Professor of Psychiatry and Cell Biology), investigated whether altered expression of the vesicular glutamate transporter 2 in rat dopamine neurons determines the resilience of these cells to rotenone, a pesticide which specifically inhibits mitochondrial complex I to selectively cause dopamine neuron loss, as a toxicant model of Parkinson’s disease.
The team found that ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra pars compacta dopamine neurons that expressed neuron vesicular glutamate transporter 2 are significantly more resilient to rotenone-induced dopamine neurodegeneration. These data suggest that vesicular glutamate transporter 2 specifically expressed in midbrain dopamine neurons boosts resilience to rotenone, but the mechanisms remain poorly characterized.
“These findings point to the vesicular glutamate transporter 2 as a new target for boosting the resilience of dopamine neurons. Therefore, our work can be used to eventually create more effective therapies to slow or even reverse the loss of dopamine neurons and improve the lives of people with Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Freyberg.
VGLUT2 Is a Determinant of Dopamine Neuron Resilience in a Rotenone Model of Dopamine Neurodegeneration
Buck SA, De Miranda BR, Logan RW, Fish KN, Greenamyre T, Freyberg Z.
Journal of Neuroscience 2 June 2021, 41 (22) 4937-4947; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2770-20.2021
